Retrieving Records - Using the SELECT Statement
Retrieving data from the database is the most general SQL operation. Database retrieval is known as a query and is performed by using SELECT statement. A basic SELECT statement holds two clauses or elements:
Select some data (column name(s)) FROM a table or more tables (table name(s)) Retrieval of records can be done in several ways:
• Selecting all records from a table
• For all records from a table Retrieving selective columns
• Selecting records based on conditions
• Selecting records in a sorted order
Let consider the first case of selecting all the records from the table.
Example
SELECT empno,empname,doj,salary FROM employee;
Here, all the column names are given in the SELECT clause. This can be additionally simplified through giving ‘*’ as follows:
Example
SELECT * FROM employee; this would display:
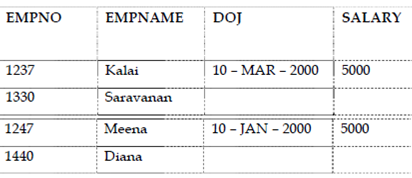
‘*’ indicates all the column names.
Note in the above description, there are no values entered in DOJ and Salary Column for the employee 1001 and 1004. The values in these columns are considered to have NULL values here. Anytime it can be updated using the Update Command.
In the other case, the column names must be specified in the SELECT statement.
Syntax
SELECT col1,col2,.. FROM <tablename>;
Example
SELECT empname,salary FROM employee; The records would be displayed as follows:
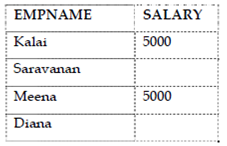
This statement retrieves the column values of salary and empname.