Barrier Measurements:
The ability of a barrier to transmit gas is commonly expressed as γ (gamma), the permeability. This is a measure of the whole flow by a barrier and might be described as the ratio of the number of molecules that pass by the barrier to the number that would pass by the space if the barrier were not there. This total flow by a barrier is known to be a combination of various different categories; namely, film flow, diffusive flow, and viscous flow. Since was previously explained then the type of flow which is of greatest importance for a gaseous diffusion plant is diffusive flow. Therefore, as film flow and viscous flow affect the separation by a barrier, they cannot be ignored.
Film flow refers to the transport of molecules under the influence of the force field among the molecules and the barrier surface. While such force fields are important, a huge number of molecules will not have enough velocity normal to the surface to escape from this field so in which their motion will be confined to the barrier surface and barrier pore surface. Like molecules would pass by the barrier as a film on the surface of the pores.
Viscous flow occurs while molecules flow as a group in the manner of usual flow through a tube. Referring back to permeability, it is called in which the flow by a barrier rise as the pressure increases. In addition, as the pressure rise, so does the viscous component of flow. The relation among permeability and viscous flow could best be display through the following equation.
γ = γo [1+S(Pf +Pb)]
In this given equation where Pf equivalent the fore or high side pressure and Pb equivalent the back or low side pressure. γo equivalent the permeability, γ , when
Pf + Pb = 0.
S is known as the slope factor and is inversely proportional to the viscosity of the gas.
In the above equation, the term S(Pf + Pb ) is a measure of the viscous elements of flow. Figure described the variation of permeability along with the slope factor and modification in pressure.
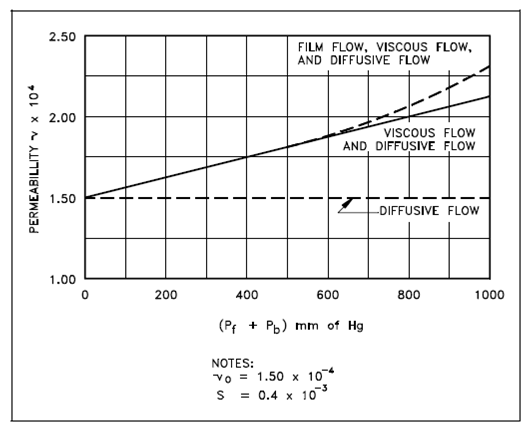
Figure: Variation of Permeability with the Slope Factor and Change in Pressure
It should be remembered that in practice, permeability is expressed in two different directions; actual and design. Design permeability is expressed as a ratio as previously stated. It is commonly determined through testing the barrier along with a non-toxic gas like as nitrogen. Actual permeability is expressed as a percentage of the design permeability and is determined from tests along with the barrier in actual operation in the cascade. Its main value is in determining the performance of a barrier after being in use for a period of time.