Potential Difference:
Potential difference is the word used to define how huge the electrostatic force is among two charged objects. The charged body will try to move in one direction if a charged body is placed among two objects along with a potential difference, depending
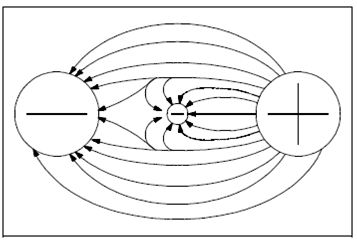
Figure: Potential Difference between Two Charged Objects
of the object upon the polarity. The action due to the potential difference is to push the electron toward the positively-charged object if an electron is placed among a negatively-charged body and a positively-charged body. An electron, being negatively charged this will be repelled from the negatively-charged object and attracted through the positively-charged object, as displayed in Figure.
Due to the force of its electrostatic field, these electrical charges have the ability to do work by moving another charged particle by attraction and/or repulsion. This capability to do work is known as "potential"; thus, if one charge is different from another, there is a potential difference among them. The sum of the potential differences of all charged particles in the electrostatic field is referred to as EMF (electromotive force).
The basic unit of measure of potential difference is the "volt." The symbol for potential difference is "V," denotes the ability to do the work of forcing electrons to move. Since the volt unit is used, potential difference is also known as "voltage." The unit volt will be covered in greater detail in the further chapter.