Photoelectric Effect:
Light is a form of energy and is considered through several scientists to consist of small particles of energy known as photons. When the photons in a light beam strike the surface of a material and they release their energy and transfer it to the atomic electrons of the material. This energy transfer might dislodge electrons from their orbits around the surface of the substance. On losing electrons, the photosensitive (light sensitive) material becomes positively charged and an electric force is created, as display in Figure.
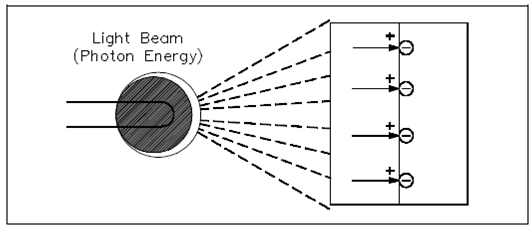
Figure: Producing Electricity from Light Using a Photovoltaic Cell
This phenomenon is known as the photoelectric effect and has huge applications in electronics, optical couplers, photovoltaic cells, like as photoelectric cells, and television camera tubes. There are Three uses of the photoelectric effect are defines below.
Photovoltaic: The light energy in one of two plates which are joined together causes one plate to release electrons to the other. The plates build up opposite charges, such as a battery that was show in the Figure.
Photoemission: The photon energy from a beam of light could cause a surface to release electrons in a vacuum tube. The plate would then collect the electrons.
Photoconduction: The light energy applied to a few materials which are generally poor conductor's cause's free electrons to be generated in the materials so in which they become better conductors.