Free Electrons:
Electrons are in rapid motion around the nucleus. Although the electrostatic force is trying to pull the nucleus and the electron both, the electron is in motion and trying to pull away. Those two effects balance and keeping the electron in orbit. The electrons in an atom exist in different energy stages. An energy stage of an electron is proportional to its distance from the nucleus. Higher energy level electrons exist in orbits, or shells, which are farther away from the nucleus. These shells nest within one another and surround the nucleus. A nucleus is the center of all the shells. The shells are lettered starting along with the shell nearest the nucleus: K, N, L, P, M, O, and Q. Every shell has a maximum number of electrons it could hold. For instance, the K shell will contain a maximum of two electrons and the L shell will hold a maximum of eight electrons. As displays in Figure, every shell has a specific number of electrons in which it will hold for a particular atom.
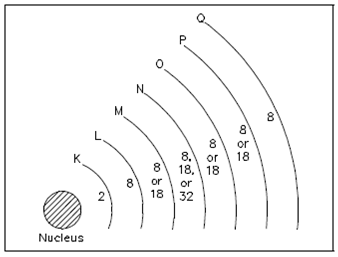
Figure: Energy Shells and Electron Quota
There are only two simple rules concerning electron shells which make it possible to predict the electron division of any element:
1. The maximum number of electrons which could fit in the outermost shell of any atom is eight.
2. The maximum number of electrons which could fit in the next-to-outermost shell of any atom is 18.
An important point to remember is that when the outer shell of an atom contains eight electrons, an atom becomes extremely stable, or very resistant to changes in its structure. Which also means the atoms with one or two electrons in their outer shell could lose electrons much more simply than atoms along with full outer shells. An electron in the outermost shell is known as valence electrons. Whenever external energy, like as heat, light, the electrons gain energy, or electrical energy, is applied to certain materials, become excited, and might move to a higher energy level. If sufficient energy is applied to the atom, a few of the valence electrons will leave the atom. These electrons are known as free electrons. It is the movement of free electrons which gives electric current in a metal conductor. An atom which has lost or gained one or more electrons is said to be ionized or to have an ion change. It becomes positively charged and is referred to as a positive ion if the atom loses one or more electrons. It becomes negatively charged and is referred to as a negative ion if an atom gains one or more electrons.