Atom:
An Element is the basic building Figure the Atom blocks of all matter. The atom is the smallest particle to that an element could be decrease although still keeping the properties of that element. The atom consists of a positively charged nucleus surrounded through negatively charged electrons, so that the atom as an overall is electrically neutral. A nucleus is composed of two types of subatomic particles, protons and neutrons, as displays in Figure. The proton carries a single unit positive charge equivalent in magnitude to the electron charge. A neutron is slighty heavier than the proton and is electrically neutral, as the name denotes. These two particles exist in several combinations, depending upon the element included. The electron is the fundamental negative charge (-) of electricity and revolves around the nucleus, of the atom in concentric orbits, or center, or shells.
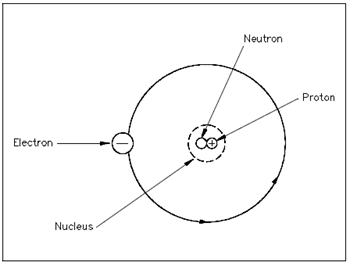
Figure: The Atom
The proton is the fundamental positive charge (+) of electricity and is situated within the nucleus. The number of protons in the nucleus of a few atoms specifies the atomic number of that atom or of that element. For instance, the carbon atom contains six protons in its nucleus; thus, the atomic number for carbon is six, as display in Figure 2.
Within its natural state, an atom of any element holds an equal number of protons and electrons. The negative charge (-) of each electron is equal in magnitude to the positive charge (+) of each proton; although, the atom is said to be electrically neutral and the two opposite charges cancel, or in balance.
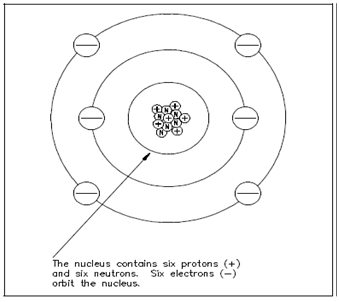
Figure: The Carbon Atom