Direct and Reverse Crank Method:
By this method, the reciprocating unbalancing may be converted into corresponding rotating unbalance by utilizing the direct and reverse crank for secondary and primary. This method is extremely useful for V-engines and radial engines.
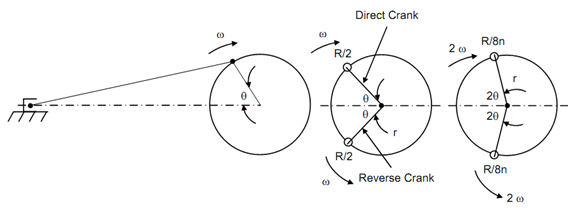
Assume there be two cranks : one direct and other reverse crank as illustrated in Figure 7(b). The net unbalance in case of primary unbalance
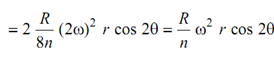
This is same as in case of reciprocating engine. Therefore, reciprocating primary unbalance is equivalent to two rotating masses each equivalent to R /2 each and rotating at radius 'r' and angular speed 'ω' however in the direct and reverse sense. Figure 7(c) represents two rotating of magnitude R /8n or R /2 at radius r/ n each rotating at angular speed '2ω' in the direct and reverse sense. The total unbalance in this case is
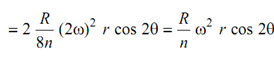
It is similar as secondary reciprocating unbalance.