Energy change:
As in a chemical reaction, nuclear reaction also involves energy change, represented by the symbol, Q. If Q is negative, the reaction is called endoergic i.e. energy is absorbed which is supplied in the form of acceleration to the bombarding particle. On the contrary if Q is positive, a reaction is known as exoergic i.e. energy is released in which case the reaction may be carried out without acceleration or at thermal temperature. The value of Q can be determined from the difference in the total masses of reactants and products of the reaction as;
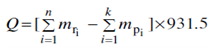
where mri = mass of reactants ri in amu,
mpi = mass of products pi in amu, and
n & k represent number of reactants and products. This is illustrated by considering the following example.
Example: Let us calculate Q value of the reaction 27Al (d, α) 25Mg
Given that masses of
27Al = 26.981541 2H = 2.014102
4He = 4.002603 25Mg = 24.985839
Sum of masses of Reactants = 26.981541 + 2.014102
= 28.995643 amu
Sum of masses of Products = 24.985839 + 4.002603
= 28.988442 amu
... Q = (28.995643 - 28.988442) × 931.5
= 6.701 MeV
Since mass of the reactants is more than that of the products, it will be an exoergic reaction. Such a reaction can take place without accelerating the bombarding particle (neutron only). Therefore, if the mass of reactants is less than which of the products, it will be an endoergic reaction. In many cases, threshold energy is required. Its calculation is illustrated in following example.