Electrophilic Substitutions of Mono-Substituted Aromatic Rings:
Ortho, Meta and para substitution
Aromatic compounds that already consist of a substituent can undergo electrophilic substitution at three dissimilar positions relative to the substituent. Refer the brominations of toluene.
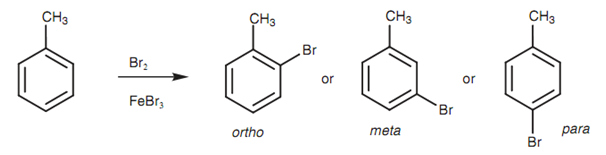
Figure: ortho, meta, and para isomers of bromotoluene.
Three dissimilar products are possible depending upon where the bromine enters the ring. These products have similar molecular formula and are hence constitutional isomers. The aromatic ring is said to be disubstituted and the three probable isomers are explained as being ortho, Meta, and para. The mechanisms leading to these three isomers are displayed in figure.
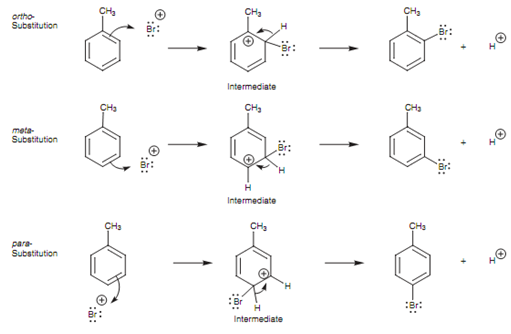
Figure: Mechanisms of ortho, Meta, and para electrophilic substitution.