Simultaneous depositions:
A mixture of copper and lead could be determined through the deposition of copper within the presence of nitrate ions at the cathode. Direct is deposited as lead dioxide at the anode.
Preparative organic chemistry:
It is then possible to reduce the starting material to the desired product through controlling the potential of the cathode during reduction if an organic compound can undergo a series of reductions (or oxidations) each at a definite potential. The category of electrolytic reduction is much more economical than chemical reductions, while side reactions generate undesired products.
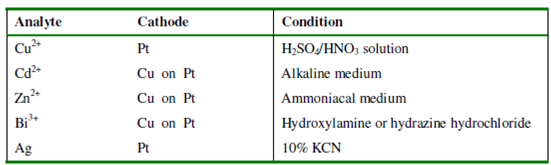
Table: Applications of controlled cathode potential electrolysis