Polyaromatic Hydrocarbons:
Silica is well suited for the separation and analysis of non-ionizing, water insoluble, and relatively simple molecules which are very closely related such as polyaromatic hydrocarbons and fats and oils with different functional groups The order of adsorption follows the general polarity scale for various classes of compounds. It is less influenced by molecular weight differences and more by specific functional groups. Therefore, the separation of compounds differing in the degree or type of alkyl substitution, such as members of a homologous series is usually by adsorption. However, adsorption chromatography has been used to isolate a number of polynuclear aromatics from a petroleum sample, as illustrated in Figure, from a totally porous silica column having dimensions of 25 × 0.46 cm and acetonitrile/water (70:30) as mobile phase.
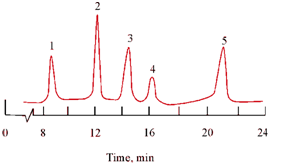
Figure: Separation of polynuclear hydrocarbons on porous and spherical silica. Peaks; 1. Naphthalene, 2. Fluorene, 3. Phenanthrene, 4. Anthracene, 5. Pyrene