Isomeric Compounds
The adsorption chromatography has a particular strength, not shared by other methods, in its ability to differentiate among the isomeric compounds in a mixture. Generally, the most polar group of a polyfunctional compound governs its adsorption characteristics. Often, only one functional group is geometrically positioned with respect to the adsorption site. However, some polyfunctional solutes are better matched to the adsorbent surface than other isomeric counterpart as typically illustrated in Figure showing the separation of positional isomers of syn- and anti- pyrazolines also called cis- and trans- forms. A 100 × 0.3 cm pellicular silica along with methylene chloride/isooctane (50:50) mobile phase was used at a flow rate of 0.225 mL/min. A fixed wavelength of 254 nm UV detector was used.
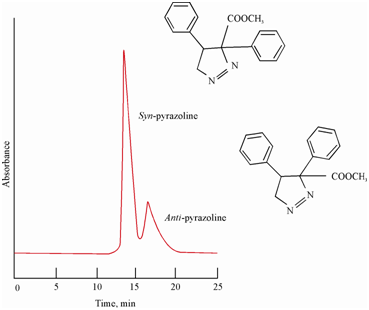
Figure: Separation of syn- and anti-pyrazoline isomers