Comparison Of Naa And Ida:
The development of analytical instrumentation over the past few decades has undergone a sea change and allowed to detect trace elements at sub-ppb or even lower levels. As recently as early 1960s, trace element determinations were predominantly carried out by traditional wet chemical methods and instrumental methods. It wasn't until the development of atomic absorption spectrophotometery (AAS) in late 1960s that the clinical community realized about necessity of a highly sensitive trace analysis technique that could be automated. With the advent of ICP technology, ICP-AES and ICP-MS were developed after 1980s. As a result NAA, AAS, and ICP-AES or ICP- MS or even XRF are in tough competition. Today NAA has emerged as a front-runner between various analytical techniques for trace element determination. A comparison of NAA with other trace element analysis methods especially with regard to size and type of samples is given in Table.
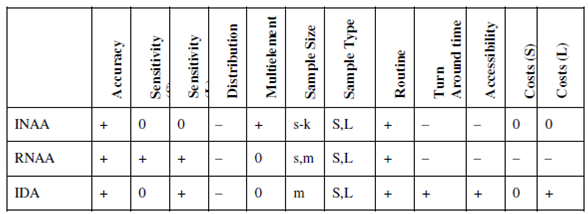
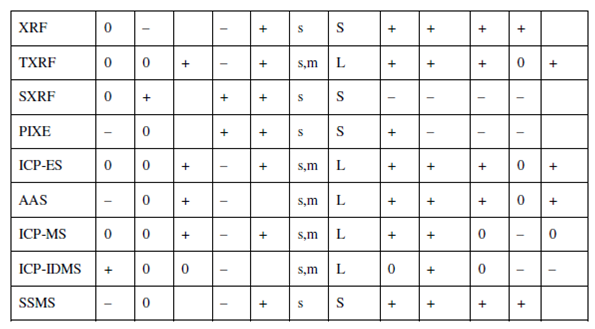
Scores: + = positive, 0 = Average, - =Negative, Sample size: s = mg, m = g, k = kg Sample type : S = solid, L = aqueous solution