Applications
Importance of trace element analysis (TEA) in today's context of technological globalization is vital. A physicist working in the field of high purity semiconductor materials, a geologist in mineral exploration, an analytical chemist dealing with the problems related to trace elements in biological systems or heavy metal pollutants in environment, a physician treating the patient suffering from a disease like Ca deficiency or Cd toxicity in bones, a curator in a museum interested in studying historical monuments and a criminologist dealing with the murder case, all require a suitable analytical technique to solve their problems at their respective work place. Though there are several alternative techniques such as x-rays fluorescence (XRF), inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), energy dispersive x-ray fluorescence (EDXRF), but the only common answer to all these problems is NAA provided a nuclear reactor is available? It is possible to determine up to 60 elements with high sensitivity, specificity, accuracy and precision. NAA has found wide applications for macro, micro, trace and ultra trace element analysis in the samples corresponding to diverse fields such as archaeology, biomedicine, animal and human tissues, environmental science, forensics, geology and cosmo chemistry, industrial products, nutrition, quality assurance of analysis and certification of reference materials (RM). Some important applications are primarily related with biology, nutrition and medicine as illustrated in Figure. NAA is now a well accepted routine analytical method for determining trace and ultra trace constituents in small size (just few mg) samples. We shall discuss some typical applications in following lines.
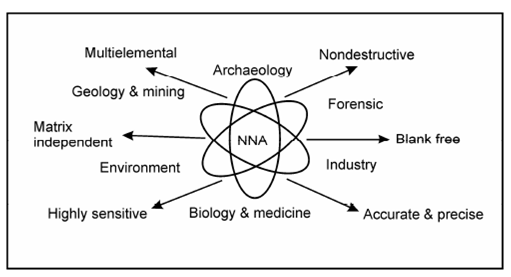
Figure: Applications of NAA in various disciplines