Fragmentation by α-cleavage in Molecules with Heteroatoms:
The bond on the carbon atom next to a herteroatom (N, O, and halogen) in a molecule is easily cleaved. This is known as α-cleavage and in such a cleavage the charge goes with the fragment containing the heteroatom. For instance, two such cleavages are display below within case of an alcohol
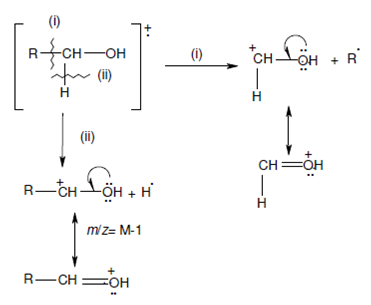
The resulting cations are resonance stabilised because of the participation of the nonbonding pair of electrons on the heteroatom as shown above.