Minimum Wage Legislation:
The minimum wage legislation entails the fixing of the wage rate for the least paid worker in the society by the government. In every modern society, such legislation is used by the government to ensure that the least paid worker have access to the basic necessities of life.
The minimum wage is reviewed regularly by every progressive government using the inflation rate trend to prevent workers standards of living from falling .The labour unions, in addition, usually clamour for upward review of the minimum wage rate to promote improvement of living standards their members.
The normal practice in the implementation of the legislation is for the government to fix the minimum wage above the equilibrium wage rate as explained in Figure
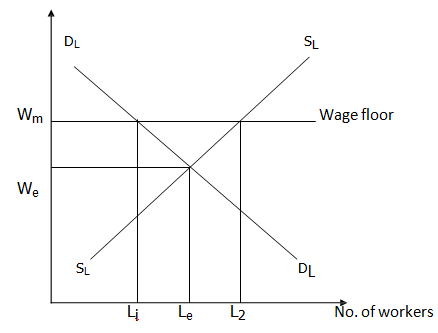
In Figure DLDL and SLSL represent demand and supply of labour services, respectively. Without government intervention, the wage rate will settle at We while Le number of workers will be employed.
However, if the government fixes minimum wage at Wm above equilibrium, the likely consequences are listed below.
i.The numbers of people willing to work at legislated wage rate Wm is greater than L1 that the labour market is able and willing to absorb i.e. excess supply of labour
ii. The problem of unemployment will worsen, precisely; Le-Li number of people will lose their jobs.
iii. There is the likelihood of labour union entering into a clandestine arrangement with their employer to receive wage rate that is less than the mandated minimum wage rate in other to prevent retrenchment of some workers.
iv. Those workers who are retained by their employer will receive higher wage rate and enjoy highest living standards given that price of goods and services remain stable in the economy.
v. It is evident from the above discussion that, for the minimum wage legislation to achieve its objectives there must be adequate job opportunities especially in the public sector of the economy.