Implementation of AIS to Assist an Adaptive Production
Control System
Immune System has represented its efficacy in different realization parts of an expert system. In this section a systematic process to apply artificial immune system to a production control and planning problem over an illustration. Hereby, a problem representing an illustration for assisting an adaptive production control system for a FMS is shown. In this difficulty, an FMS consists of three machine families as F1, F2, and F3, three loads or unload stations as L1, L2, and L3, three automatic guided vehicles as A1, A2, A3, an input buffer, a centralized buffer that is utilized for avoidance of deadlock. A local region network is employed for inter-connecting all equipment. Eleven various parts type are being processed in the FMS. The processing time for all of 11 part type at each load or unload station and at all machine family is taken not same. A continuously altering five various part mix ratios are taken in the account for seeking the various conditions of bottlenecks that is given in Table no.3.
Table no.3: Part Mix Ratios
|
Part type
|
Part Mix Ratios (%)
|
|
|
Mix 1
|
Mix 2
|
Mix 3
|
Mix 4
|
Mix 5
|
|
1
|
11.00
|
14.00
|
6.00
|
9.00
|
14.00
|
|
2
|
11.00
|
14.00
|
6.00
|
9.00
|
14.00
|
|
3
|
11.00
|
15.00
|
6.00
|
9.00
|
14.00
|
|
4
|
12.00
|
10.00
|
15.00
|
8.00
|
15.00
|
|
5
|
6.00
|
12.00
|
15.00
|
13.00
|
7.00
|
|
6
|
8.00
|
8.00
|
9.00
|
12.00
|
5.00
|
|
7
|
8.00
|
5.00
|
8.00
|
3.00
|
5.00
|
|
8
|
7.00
|
3.00
|
8.00
|
9.00
|
4.00
|
|
9
|
7.00
|
3.00
|
7.00
|
8.00
|
4.00
|
|
10
|
2.50
|
1.00
|
4.00
|
1.00
|
6.00
|
|
11
|
16.50
|
15.00
|
16.00
|
19.00
|
12.00
|
The problem has given assumptions that are no delay into the availability of raw material, one part type for all jobs order, execution of merely one job order at time upon a machine, processing time taken is preselected, all part type is processed via a predetermined sequence, a part type should go back to the load or unload station after finishing all machining operation or to central movement and the buffer of materials whether AGVs are as negligible.
In this difficulty, the performance criteria are throughput and mean flow time as represented in Table no.4 that depends on the various system attributes and various dispatching rules. Each the system dispatching and attributes rules along with mathematical formulations and the occupied notations are represented in the following Tables in Tables no.5 and 6. The notations occupied are explained in Table 10.7.
Table no.4: Performance Criteria
|
Performance
Criteria
|
Description
|
Mathematical
Formulation
|
|
TP
|
Throughput
|
| sf |
|
|
MF
|
Mean Flow Time
|
∑ i ∈sf fi
| sf |
|
Table no.5: System attributes
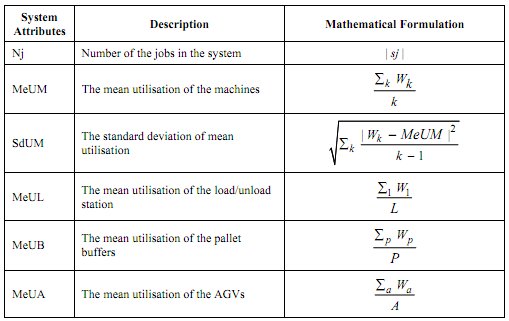
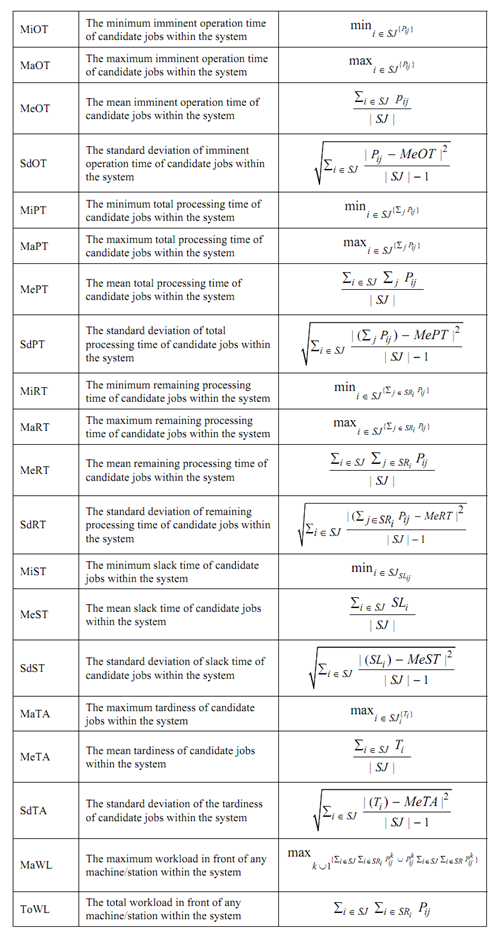
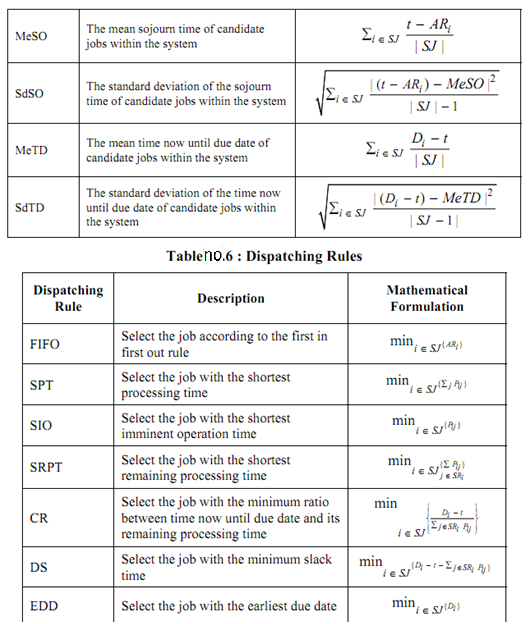
Table no.7: Notations
|
Notation
|
Description
|
|
i
|
Job index
|
|
j
|
Operation index
|
|
k
|
Machine index (K = number of machines)
|
|
t
|
Time when decision is to be made
|
|
a
|
AGV index (A = number of AGVs)
|
|
l
|
Load/unload station index (L = number of load /unload stations)
|
|
p
|
Pallet buffer index (P = number of pallet buffers)
|
|
Wk
|
Percentage of work time on machine k in a scheduling period
|
|
Wl
|
Percentage of work time on load/unload l station in a scheduling period
|
|
Wa
|
Percentage of work time on AGV a in a scheduling period
|
|
Wp
|
Percentage of work time on pallet buffer p in a scheduling period
|
|
Pij
|
Processing time of the jth operation of job i
|
|
Pkij
|
Processing time of the jth operation of job i in machine k
|
|
Plij
|
Processing time of the jth operation of job i in load/unload station l
|
|
ARi
|
Time when job i arrives at the system
|
|
Di
|
Due date of job i
|
|
Ci
|
Time when job i is completed and leaves the system
|
|
SJ
|
Set of jobs within the system
|
|
SF
|
Set of finished jobs
|
|
SRi
|
Set of remaining operation of job i
|
|
|SJ|
|
The cardinality of SJ
|
|
|SF
|
The cardinality of SF
|
|
Fi
|
Flow time of job i (Fi = Ci - ARi)
|
|
Ti
|
Tardy time of job I (Ti = max (0, Ci - Di))
|
|
SLi
|
Slack time of job I (SLi = Di - t - ∑ j ∈SR Pij )
i
|