Recombination of heavy chain genes
The Heavy chains are synthesized in an analogous manner but are encoded through four gene segments that are, V, J, D and C in above figure. In humans, there are 51 VH segments 27 DH segments where D for diversity and H for heavy and six JH segments. Therefore, where the
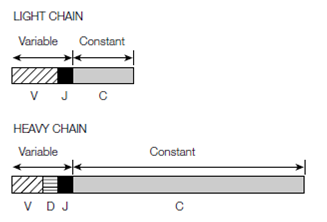
Figure: The light chain variable region is encoded by two separate gene segments, V and J. The heavy chain variable region is encoded by three gene segments, V, D and J.
variable region of a light chain polypeptide is encoded through V and J segments the variable region of a heavy chain is encoded via V, D and J segments. In humans connecting any of D, V, and J segments generates 51×27× 6 = 8262 probable heavy chain variable regions. In heavy chain gene system, there are also various C segments, one for each class of heavy chain; Cµ, Cδ, the several Cγ subclasses, Cε and Cα encoding µ ,α, ε, γ and δ heavy chain constant regions respectively. During lymphocyte maturation, two heavy chain gene rearrangements happen. First a chosen DH segment joins a JH segment (DJ joining) and then the recombined DHJH joins a chosen VH segment (VDJ joining).
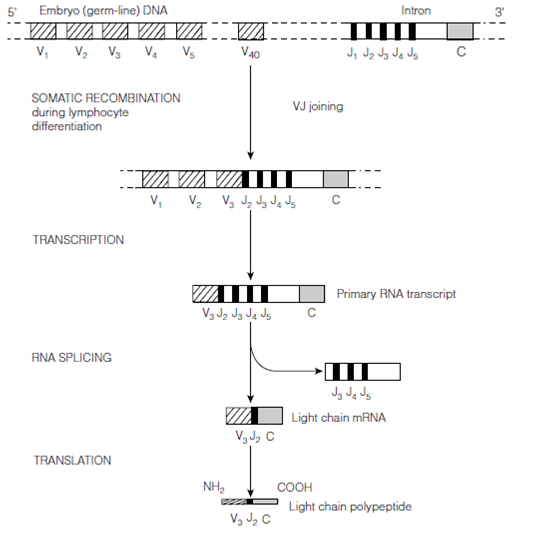
Figure: Somatic recombination to create a human light chain gene and expression of that gene to produce light chain polypeptides.
For the assembly of both light chain and heavy chain genes, the ends of the several DNA segments to be joined can also undergo modification in during the recombination procedure and this modifies existing codons at these junctions or even establish new codons, therefore increasing antibody diversity since further. Additionally, antibody genes exhibit a higher than normal rate of mutation.