Fab and Fc fragments
Papain, a protease, cuts the immunoglobulin G molecule to release the two arms of the Y-shaped molecule, every of that has one antigen-binding site and is known as an Fab fragment Fragment antigen binding. Hence Fab fragments have only one antigen-binding site for instance is univalent, they cannot cross-link antigens. The defined stem of the Y-shaped molecule which is consisting of the identical C-terminal components of the two H chains is named the Fc fragment because it readily crystallizes. The fragment Fc carries the effector sites which switch the destruction of the antigen, for instance triggering of the complement system and inducing phagocytosis of pathogens through other white blood cells. In contrast to pepsin, papain, (another protease) cuts the immunoglobulin G molecule to release the two arms of immunoglobulin G since linked together and therefore this fragment has two antigen-binding sites example is bivalent and can still cross-link antigens. This is known as the F (ab) 2 fragments.
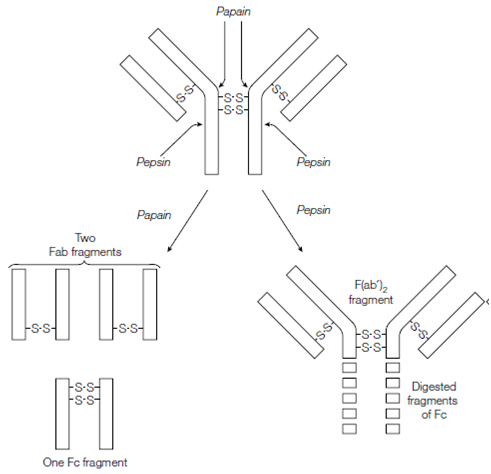
Figure: Papain digestion of an antibody molecule yields two univalent Fab fragments and an Fc fragment whereas pepsin digestion yields a bivalent F(ab )2 fragment.