The Elements of the Analysis Model
Analysis model must achieve 3 primary goals: (1) to define what the customer needs, (2) to build a basis for the establishment of a software design and (3) to describe a group of needs which can be validated once the software is established. To complete the analysis model derived during structured analysis takes the form which describe in figure.
At the core of the model lies the data dictionary a repository which contains information of all data objects produced or consumed through the software. 3 several diagrams surround the core. Entity- relationship diagram that is also known as ERD depicts relationships among data objects. The ERAD is the notation which is used to conduct the data modeling activity. The attributes of each data object was noted in the ERD can be elaborate using a data object description.
The data flow diagram describes 2 purposes that are: (1) to give an indication of how data are transformed as they move by the system and (2) to depict sub function and the functions which transform the data flow. DFD gives additional information which is used during the analysis of the information serves and domain as a basis for the modeling of function. The description of each function presented in the DFD is contained in a procedure specification (PSPEC).
The STD that is state-transition diagram indicates how the system behaves as a consequence of external events. To accomplish this STD represents the several are made from state to state. The STD presents as the basis for behaviour called states of the system and the manner in that transitions are made from state to state. The STD serves as the basis for behavioural modeling. While description about control aspects of the software is contained in the control specification
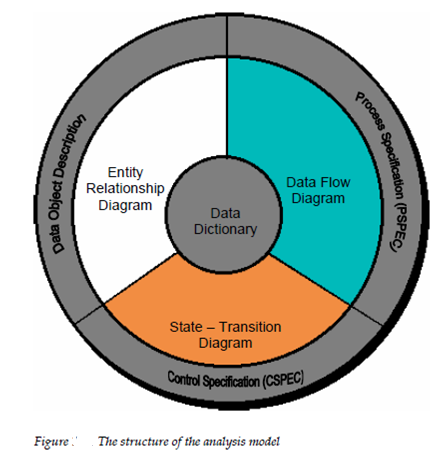
Analysis model encompasses every diagram specifically, descriptions and the dictionary noted give more detailed discussion of these parts of the analysis model is presented in the sections which follow.