Creating a Control Flow Model
For many kinds of data processing applications the data model and the data flow diagram are all which is necessary to obtain important insight into software needs. As we have already noted moreover there exists a huge class of applications which are driven through events rather than data which produce control information rather than reports or displays and which process information with heavy concern for time performance. Like application need the use of control flow modeling in addition to data flow modeling.
The graphical notation needs to build a control flow diagram CFD was presented. To review the approach for building a CFED a data flow model is stripped of all data flow arrows10 control items and Events dashed arrows are then added to the diagram and a window a vertical bar into the control specification is described below but how are events selected?
We have previously noted that a control or event item is implemented as a Boolean value example for true/ false, on/ off, 1 / 0 or a discrete list of conditions jammed empty, full. To select potential candidate events the following guidelines are suggested.
- List all sensors which are read through the software
- List all interrupt conditions
- List all switches which are actuated through an operator
- List all data conditions.
- Recalling the noun-verb parse which was applied to the processing narrative review all control items as possible CSPEC inputs or outputs
- To describe the behavior of a system through identifying its states; identify how each state is define and reached the transitions among states.
- Consider on possible omissions a very common error in specifying control example for asks: Is there any other way I can get to this state or exit from it?
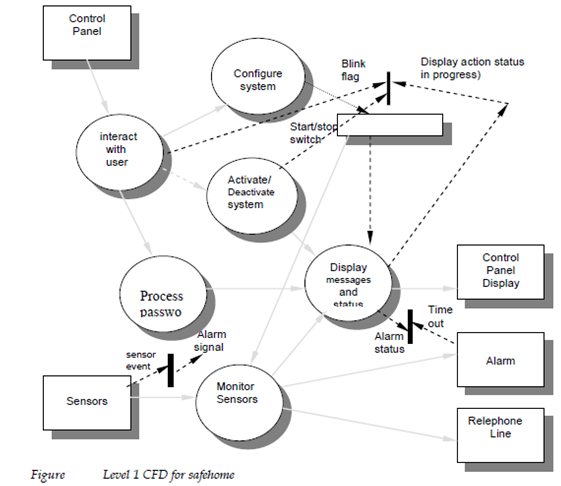
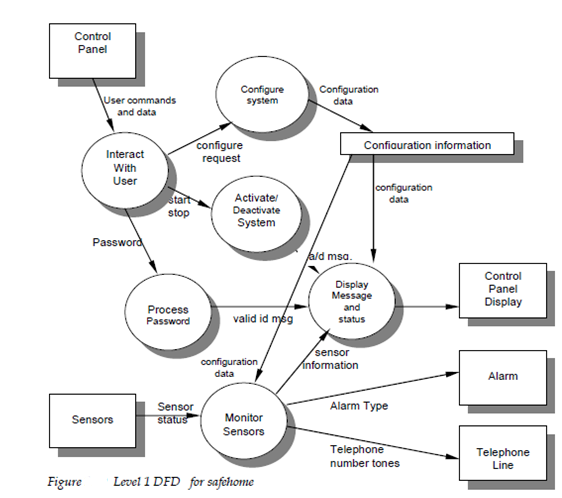
A level one CFD for Safe Home software is described in Figure 16.11 Between the control and events items noted are sensor event example for a sensor has been tripped blink flag a signal to blink the LCD display, start or stop switch a signal to turn the system on or off An event flowing into the CSPEC window from the outside world implies in which the CSPEC will activate one or more of the processes shown in the CFD. When a control item emanates from a procedure and flows into the CSPEC control, window and activation of some other procedure or an outside entity is implied.