Attributes
Attributes describe the properties of a data object and take on one of 3 various characteristics. They can be used as a (1) name an instance of the data object, (2) define the instance or (3) make reference in another table to another instance in. In addition one or more of the attributes must be described as an identifier which is the identifier attribute becomes a key when we need to search an instance of the data object. In various cases, values for the identifiers are unique, while this is not a need. Referring to the data object car a reasonable identifier might be the ID#
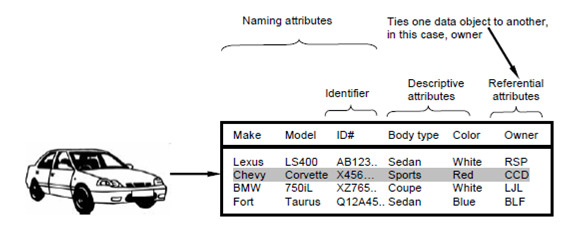
Figure - Tabulator representation of data objects
By the group of attributes which is appropriate for a given data object is determined by an understanding of the problem context. The attributes for car define above might serve well for an application which would be used through a Department of Motor Vehicles but these attributes would be useless for an automobile organization which needs manufacturing control software. In Later case the attributes for car might also include body type, ID#, color but several additional attributes example for interior code, trim package designator, driver train type, and transmission type would have to be added to make car a meaningful object in the manufacturing control circumstance.