Hydrophobic, Aliphatic Amino Acids
Glycine (Gly or G) ,the smallest amino acid with the easiest structure, has a hydrogen atom in the side-chain position, and therefore does not exist as a pair of stereoisomers as there are 2 identical groups (hydrogen atoms) associated to the Cα atom. Aliphatic side chains of alanine (Ala or A), leucine (Leu or L), valine (Val or V), methionine (Met or M) and Fisoleucine (Ile or I) are chemically unreactive, but in nature hydrophobic . Proline (Pro or P) is
(a)
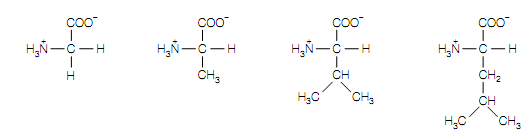 Glycine Alanine Valine Leucine
Glycine Alanine Valine Leucine
(Gly, G) (Ala, A ) (Val, V) (Leu, L)
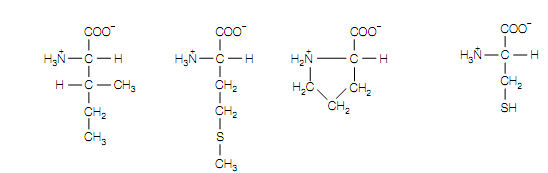 Isoleucine Methionine Proline Cysteine
Isoleucine Methionine Proline Cysteine
(Ile, I) (Met, M) (Pro, P) (Cys, C)
(b)
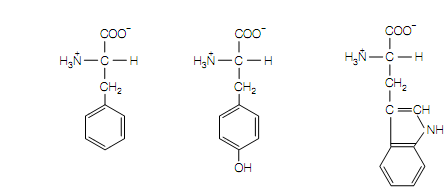
Phenylalanine Tyrosine Tryptophan
(Phe, F) (Tyr, Y) (Trp, W)
The standard amino acids (a) Hydrophobic, aliphatic R groups, (b) hydrophobic, aromatic R groups
also hydrophobic but, on to the amino group ,with its aliphatic side-chain bonded back, it is conformationally inflexible. The sulfur containing side chain of cysteine (C or Cys) is hydrophobic also and is greatly reactive, capable of reacting along another cysteine to form a disulfide bond.