Excitatory amino acids
The Aspartate and Glutamate are the main CNS excitatory transmitters with glutamate by nearly all the predominant. Most of the main sensory pathways and a few motor pathways are glutamatergic as shown in table below. Out of the pyramidal cells in the granule cells and cerebral cortex the cerebellar cortex release the glutamate.
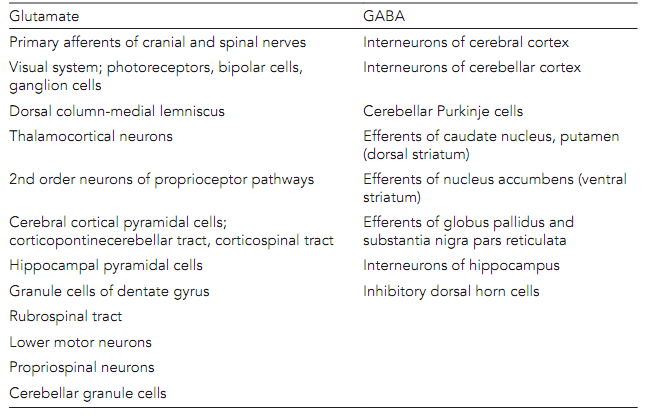
Table: Major glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons/pathways
The Neurotransmitter glutamate is synthesized in the neurons from glutamine, which is a reaction catalyzed by glutaminase. The Glutamate is then pumped into vesicles. After releasing the glutamate eliminated from the synaptic cleft by glutamate transporters in neurons and glial. In neurons the glutamate is probably metabolized, however some might be recycled as a transmitter. At glia the glutamate is converted by the glutamine synthetase to glutamine that is then liberated into the extracellular space for uptake by neurons. This closes the glutama glutamine cycle as shown in figure below. It permits astrocytes to export transmitter glutamate to neurons in a form—glutamine—which cannot spuriously activate the glutamate receptors.
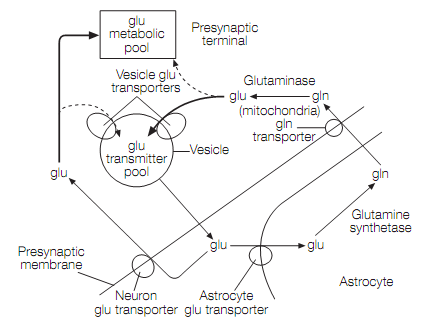
Figure: The glutamate (glu)–glutamine (gln) cycle.
The Glutamate acts on ionotropic receptors—AMPA, kainate, and NMDA, named for select antagonists—that are cation conductances, and on metabotropic receptors (GPCRs).