Pyridoxal phosphate:
The coenzyme (or prosthetic group) of all transaminases is pyridoxal phosphate, which is derived from pyridoxine (vitamin B6), and which is transiently converted into pyridoxamine phosphate during transamination shown in the figure. In the absence of substrate, the aldehyde group of pyridoxal phosphate forms a covalent Schiff base linkage (imine bond) with the amino group in the side- chain of a specific lysine residue in the active site of the enzyme. On further of
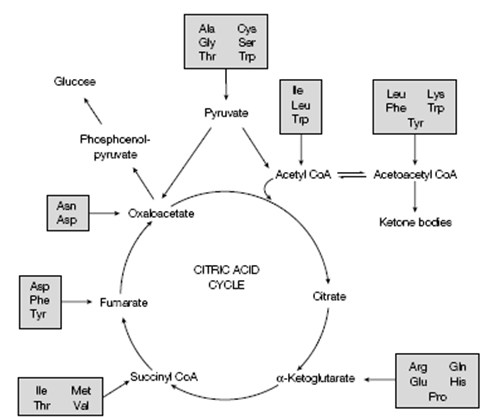
Figure: Fates of the amino acid carbon skeletons.
substrate, and the α-amino group of the incoming amino acid displaces the amino group of the active site lysine and a new Schiff base linkage is formed with the amino acid substrate. The resulting amino acid-pyridoxal phosphate-Schiff base that is formed remains tightly bound to the enzyme through multiple noncovalent interactions.
The amino acid is then hydrolyzed to form an pyridoxamine and α-keto acid
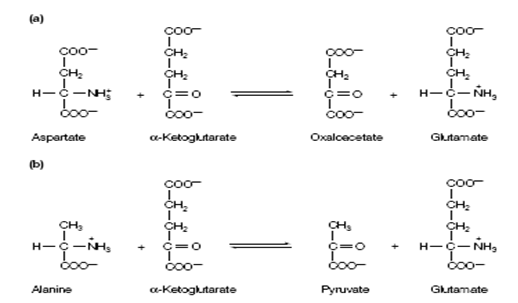
Figure: Reactions catalyzed by (a) aspartate transaminase and (b) alanine transaminase
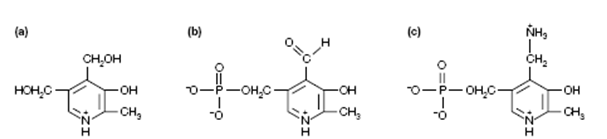
Figure: Structures of (a) pyridoxine (vitamin B6), (b) pyridoxal phosphate and (c) pyridoxamine phosphate.
phosphate, the α-amino group having been temporarily transferred from the amino acid substrate on to pyridoxal phosphate described in above figure. This step constitutes one half of the whole transamination reaction. The second half occurs through a reversal of the above reactions with a second α-keto acid reacting with the pyridoxamine phosphate to yield a second amino acid and re produce the enzyme-pyridoxal phosphate complex.
The reactions catalyzed through transaminases are anergonic as they do not needed an input of metabolic energy. They are also freely reversible, the way of the reaction being determined through the relative concentrations of the amino acid-keto acid pairs. The Pyridoxal phosphate is not just used as the coenzyme in transamination reactions but is also the coenzyme for various other reactions
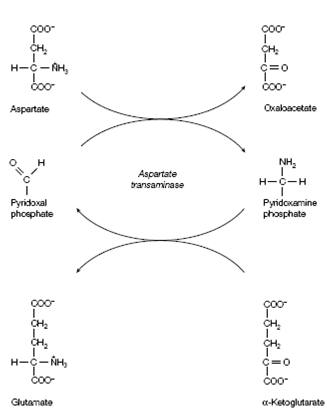
Figure: The overall reaction of transamination
including amino acids involving decarboxylations, racemizations, deaminations and aldol cleavages.