Oxidative deamination of glutamate:
The α-amino groups which have been funneled into glutamate from the other amino acids are then converted into ammonia through the action of glutamate dehydrogenase. This enzyme is extraordinary in being able to utilize either NADP+ or NAD+. In the biosynthesis of glutamate the NADP+ form of the coenzyme is used, while NAD+ is used in its degradation. The Glutamate dehydrogenase consists of six identical subunits and is subject to allosteric regulation. ATP and GTP are allosteric inhibitors, while GDP and ADP are allosteric activators. Therefore, wshen the energy charge of the cell is low instance example there is more GDP and ADP than their triphosphate forms) glutamate dehydrogenase is activated and the oxidation of amino acids increases. The concluding carbon skeletons are then utilized as metabolic fuel, feeding into the citric acid cycle and ultimately giving rise to energy through oxidative phosphorylation.
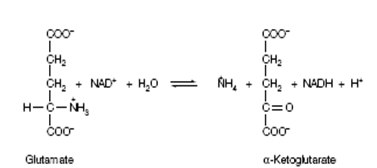
Figure: Oxidative deamination of glutamate by glutamate dehydrogenase.