Amino acid oxidases:
The main route for the deamination of amino acids is transamination followed of glutamate through the oxidative deamination. Moreover, a minor route also exists which includes direct oxidation of the amino acid through L-amino acid oxidase. This enzyme utilizes FMN (flavin mononucleotide) as its coenzyme, with the resulting FMNH2 being reoxidized through molecular O2, a procedure which also produce the toxic H2O2. The H2O2 is rendered harmless through the action of catalase. Liver and Kidney are also rich in the FAD-containing D-amino acid oxidase. Moreover, the function of this enzyme in animals is unclear, because the
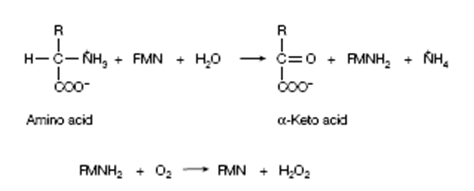
Figure: Action of L-amino acid oxidase.
D-isomers of amino acids are rare in nature and only occurring in certain antiobiotics and. bacterial cell walls