Game theoretic models:
The theory of games developed by Neuman and Morgensten is an alternative approach that has been applied to market situations where there is interdependence in the course of action. Many decision problems of oligopolistic firms have been solved by applying the method of game theory.
We will discuss with same details of game theory in Block 8. Before it is done, let us get familiar with some of its concepts to be able to appreciate the solution mechanism offered in the select models of alternative theories of firm. In a game, there are two participants called players, and it is assumed that each player knows all the possible course of action of all. Each particular course of action is called a "strategy" and associated with each strategy is a "pay-off".
Definitions:
1) Strategy: In game theory, a strategy is a specific course of action with clearly defined values for the policy variables. For example, a strategy may consist of setting a price of X, spending of Y on advertising, making a change in packaging of product etc. In game theory these strategy are generally devoted by alphabets or alphanumeries (A1, A2, ....). strategies can be of two types: pure strategies mixed strategies.
a) Pure strategies - In this format, the players choose a particular strategy with probability 1.
b) Mixed strategies - In this case, each player plays her strategies accordingly to a predetermined set of probabilities.
2) Pay-off - The pay-off of a strategy is the 'net gain' it will bring to the firm for any given counter-strategy of the competitor. This gain is measured in terms of the goals of the firm. For example, if the goal of the firm is to maximise its profits, then the pay-off of a strategy will be measured in terms of project levels that yield the maximum.
The pay-off matrix of a firm would be a table showing the gains accruing to the firm as a result of each possible combination of strategies adopted by it and its rival. Suppose there are two firms - A and B. A has three strategies while B has four. Thus, there will be 3 × 4 = 12 pay-offs, as shown in the following
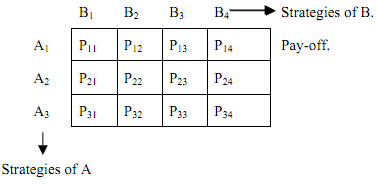
3) Equilibrium of a game - It is a strategy combination consisting of the best strategy for each player, when neither one has any incentive to deviate. It is called a Nash-equilibrium.