Phase Opposition:
Whenever two sine waves start exactly one-half cycle, or 180°, separately, they are said to be in phase opposition. It is demonstrated by the drawing of figure shown below. When two sine waves have similar amplitude and are in phase opposition, they cancel each other out since the instantaneous amplitudes of the two waves are equivalent and opposite at each and every moment in time.
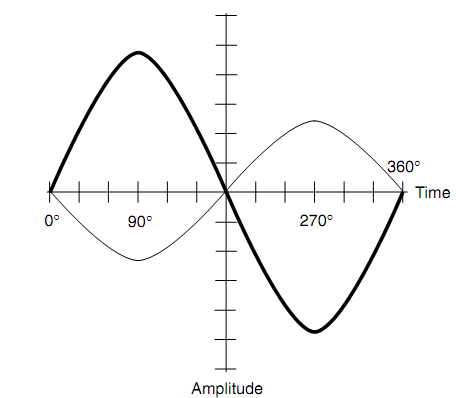
Figure: Two sine waves in phase opposition.
When two sine waves have distinct amplitudes and are in phase opposition, the peak value of the resultant wave, that is a sine wave, is equivalent to the difference among the peak values of the two composite waves. The phase of the resultant is similar as the phase of the stronger of the two composite waves.