Bond rotation:
This bond includes
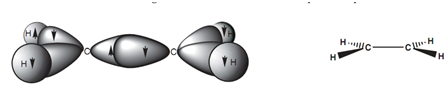
Figure: (a) σ bonding diagram for ethene; (b) simple representation of σ bonds for ethene.
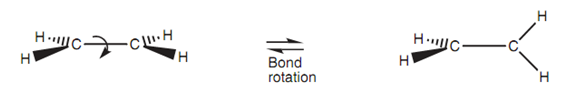
Figure: Bond rotation around a σ bond.
The remain half-filled 2py orbitals on each carbon that overlap side-on to produce a pi (p) bond), with one lobe over and one lobe under the plane of the molecule. This π bond avoids rotation round the C-C bond because the π bond would have to be broken to permit rotation. A π bond is weaker as compared to an σ bond because the 2py orbitals overlap side-on, resultant in a weaker overlap. The existence of a π bond also describes why alkenes are more reactive as compared to alkanes, because a π bond is more easily broken and is more likely to take part in reactions.
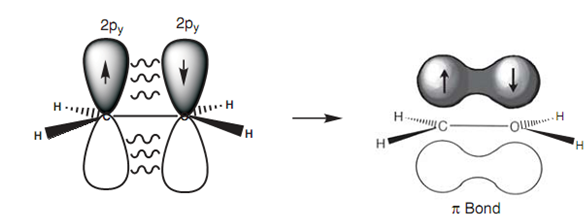
Figure: Formation of a π bond.