Characteristics of Adhesives and Adhesive Joints
While an adhesive joint is created it ought to show one or several of following properties.
1. Mechanical strength against shear & peel.
2. Toughness or resistance to impact.
3. Resistance to heat and moisture and other environmental degrading actions.
4. Resistance to many fluids and chemicals.
5. Capability to spread evenly on surfaces to be jointed – wetting property.
A large number of adhesives are available commercially. Many of them have been named earlier. Properties of a few are explained in Table.
Table: Typical Properties of Some Commercial Adhesives
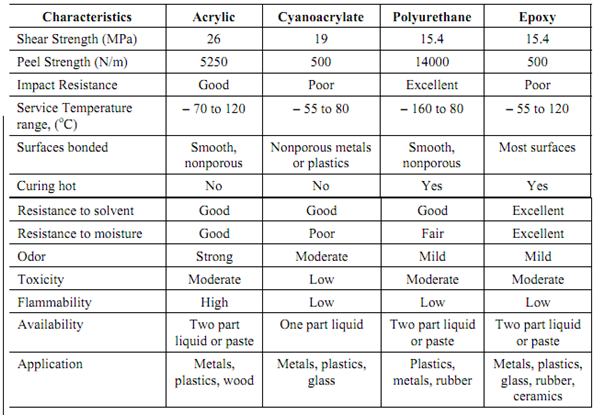
Though adhesives have convenience of joining similar & dissimilar metallic and non-metallic materials of distinct shapes and size the application is restricted because of special care and skill needed for design of joint and bonding methods. Service temperature is highly restricted. Curing time is still another significant factor to be considered for it might range from a few seconds at higher temperature to various hours at room temperature. Thermosetting adhesives need long curing time.
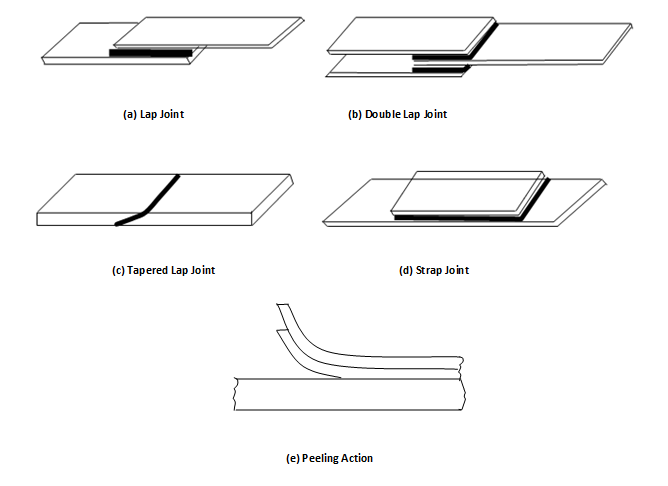
Designer should ensure that the joints are subjected to, tension, compression or shear but not subjected to peeling force. Single lap, tapered lap (scarf), double lap, and butt (strap) joints and peeling action are illustrated in Figure. The production of these joints shall require special fixtures, presses, autoclaves, toolings and ovens for curing. Various industries have developed such special skills and high level of facilities for generating adhesive joints. Automotive, building products, aerospace and appliances industries use these joints extensively. Attaching rear view mirror to windscreen of car, automotive brake lining assemblies, helicopter blades, laminated wind shield glass, aircraft bodies are a few examples where adhesive bonding is used.