Tautomerism:
Tautomerism is the word that used to describe the rapid interconversion of two dissimilar isomeric forms (tautomers) - in this case the keto and enol tautomers of a ketone. The keto tautomer is by far the dominant species for a ketone and the enol tautomer is generally present in only extremely small amounts (usually 0.0001%). Hence, as soon as the enol is created in the above reaction, it quickly tautomerizes to the keto form and further electrophilic addition does not occur.
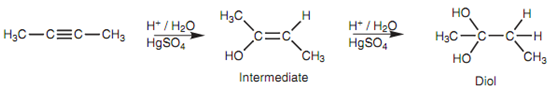
Figure: Reaction of 2-butyne with aqueous acid and mercuric sulfate.
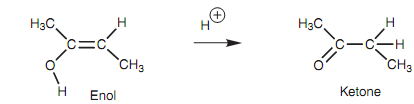
Figure: Keto-enol tautomerism.