Reaction of 2-butyne:
Treatment of an alkyne along with one equivalent of HBr provides a bromoalkene. If two equivalents of hydrogen bromide are exists the reaction can go two times to give a geminal dibromoalkane in which both bromine atoms are added to similar carbon.

Figure: Reaction of 2-butyne with (a) 1 equivalent of HBr; (b) 2 equivalents of HBr.
The above addition reactions are identical to the alkenes' addition reactions. Though, the reaction is much slower for an alkyne, because alkynes are less reactive. One might expect alkynes to be more nucleophilic, because they are more electron rich in the vicinity of the multiple bonds, i.e. six electrons in a triple bond compared to four in a double bond. Though, electrophilic addition to an alkyne includes the creation of a vinylic carbocation. This carbocation is much less stable as compared to the carbocation intermediate resultant from electrophilic addition to an alkene.
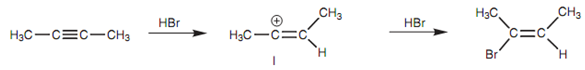
Figure: Electrophilic addition to an alkyne via a vinylic carbocation (I).
Because of this low reactivity, alkynes react slowly with aqueous acid, and mercuric sulfate has to be added like a catalyst. The product that might be supposed from this reaction would be a diol. Actually, a diol is not created. The intermediate (an enol) goes through acid catalyzed rearrangement to provide a ketone instead. This process is termed as a keto-enol tautomerism.