Representation of active transport in cell membranes:
Enzyme E1 near the surface of low concentration of A promotes the chemical reaction among A and B to yield a compound AB inside the cell membrane. Compound AB will diffuse by the membrane to the other side whereas there is another enzyme E2.This enzyme does just the opposite of what E1 does and expedites the decomposition of AB within A and B.
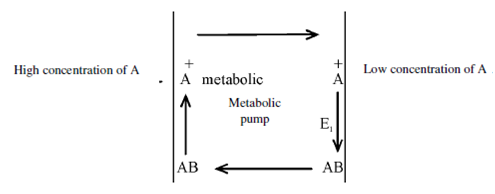
Figure: A schematic representation of active transport in cell membranes
The element A diffuses out of the membrane to the high concentration side since there is a local build up of A inside the membrane. A carrier molecule B is too large to pass by the cell membrane and is holed inside the membrane. The two enzymatic reactions constitute a metabolic pump that produced power to pump A against its concentration gradient. The accumulation of potassium ions in cells is a well known instance of active transport.