Propagation of action potentials
In neuron, the action potentials are initiated at axon hillock since this area has the greatest density of Navs and therefore the lowest threshold. And hence the axon hillock is also termed as the spike initiation zone. Once it is generated, and then action potentials are actively propagated (or conducted) with constant velocity down the axon without the loss of amplitude. Therefore, action potentials are undiminished in size even when conducted along the peripheral axons which in humans may be up to one meter long. This is one of the features which make action potentials reliable signals for information transmission. The particulars of conduction are a little different depending on whether the neuron is myelinated or not.
In nonmyelinated, the neurons conduction works as follows as shown in figure. The area of an axon occupied by an action potential at a given time is known as the active zone. It is a few cm long. The section of the active zone occupied by the overshoot of the spike will be inside and is positive. So Far from the active zone, ahead of the oncoming action potential or behind it, the membrane potential will be inside is negative. The effect of this is that a potential difference exists between various segments of axon membrane and therefore local circuit currents flow passively between these axon segments.
Ahead of the axon potential the currents drain positive charge from the external surface of the axon and concurrently dump positive charge on the inside of the axon membrane. The total effect is to depolarize the axon instantly in front of the action potential. Whenever this depolarization becomes suprathreshold Navs in this area activate and the action potential advances. Obviously, local circuit currents flow in similar way along the axon behind the action potential but this area is refractory and hence, the currents do not excite here. Therefore action potentials propagate physiologically only in one direction.
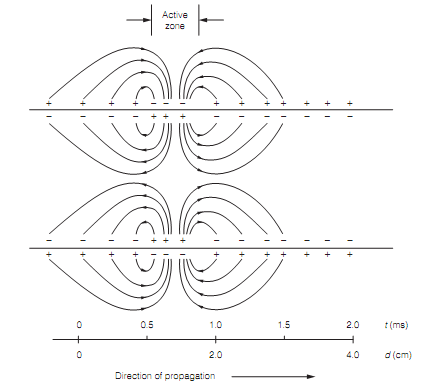
Figure: Local circuit currents in action potential conduction. The action potential is traveling from left to right and the leading edge of the spike (i.e., active zone) is 2 cm from the origin (lower scale) after 1 ms (upper scale). t is the time; d is the distance. By the convention current direction is the flow of positive charge.