Sound waves
Sound is the oscillation of atoms or molecules in a compressible medium. The energy of oscillations is transmitted as a longitudinal wave in which the medium is alternately rarefied and compressed, causing periodic variations in the pressure of the medium as shown in figure below:
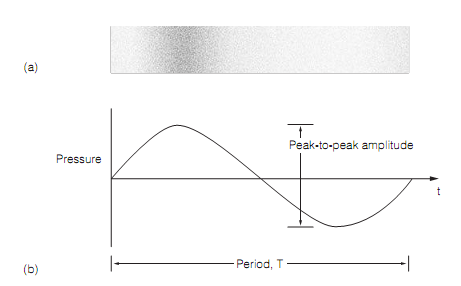
Figure: Sound waves: (a) density of air molecules during propagation of a longitudinal pressure wave; (b) sine wave representation of a pressure wave.
For a sine wave the period, T, is the time taken for one complete cycle. The frequency of the wave, perceived pitch of the sound, is the reciprocal of the period (that is., f = 1/T). The unit of frequency is the Hertz (Hz); one cycle per second.