Ionization of amino acids
Introduction: The α-carboxyl and α-amino groups on amino acids act as acid–base groups, donating or accepting a proton as the pH is altered. Both groups are fully protonated, at low pH, but as the pH is increased first the carboxyl group and then the amino group loses a hydrogen ion. The pK is in the range 1.8–2.9 for the α-amino group for the α-carboxyl group and 8.8–10.8 for the standard 20 amino acids. Those amino acids with an ionizable side-chain are having an additional acid–base group with a distinctive pK.
The twenty standard amino acids contain two acid–base groups: the α- carboxyl and α-amino groups associated to the Cα atom. Those amino acids with an ionizable side-chain (Glu, Asp, Lys, Arg His, Tyr ,Cys) have an additional acid–base group. The titration curve of Gly is shown in given figure. At low pH (for example high hydrogen ion concentration) both the amino group and the carboxyl group are completely protonated so that in the cationic form H3 N + CH2 COOH the amino acid is .As in solution the amino acid is titrated with increasing amounts of a strong base (for example NaOH), it loses 2 protons, ?rst from the carboxyl group which has the lower pK value (pK = 2.3) and then from the amino group which has the higher pK value (pK = 9.6). The pH at which Gly has no net charge is termed its isoelectric point, pI. The α-carboxyl groups of all the twenty standard amino acids contain pK values in the range 1.8–2.9, whereas their α-amino groups contain pK values in the range 8.8–10.8 .The side-chains of the acidic amino acids Glu and Asp contain pK values of 4.1 and 3.9, respectively, whereas those of the basic amino acids Arg and Lys, contain pK values of 12.5 and 10.8, respectively. The side-chain of His, Only with a pK value of 6.0, is ionized within the physiological pH range (pH 6–8). It should be kept in mind that when the amino acids are attached together in proteins, the side-chain groups and the terminal α-amino and α-carboxyl groups are free to ionize only.
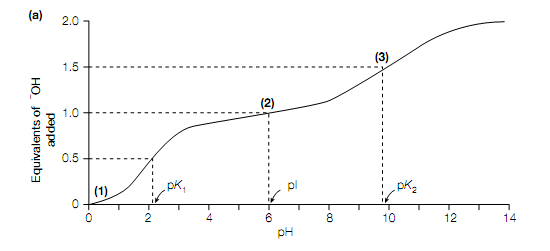
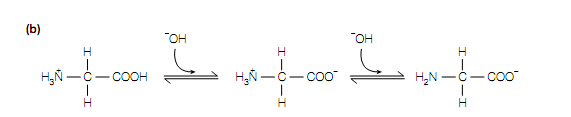
Ionization of glycine. (a) Titration curve of glycine, (b) dissociation of glycine. Numbers in bold in parentheses in (a) correspond to the structures in (b).
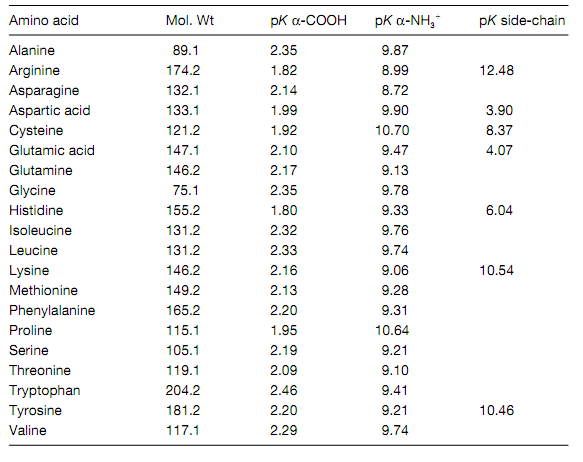
Table: pK values and molecular weights of the 20 standard amino acids