Buffers
An acid-base conjugate pair may act as a buffer, resisting changes in pH. The inflexion point indicates the pK value from a titration curve of an acid. The buffering capacity of the acid-base pair is the pK ± 1 pH unit. The carbonate and phosphate ions act as buffers in biological fluids. Also Proteins, Amino acids nucleic acids and lipids have some buffering capacity. In the laboratory other compounds, like TRIS, are used to buffer solutions at the suitable pH.
An acid-base conjugate pair, like acetate and acetic acid, is able to resist changes in the pH of a solution. That is, it may act as a buffer. On addition of hydroxide (OH-) to a solution of acetic acid the following will happens:
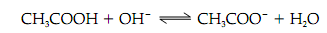
on the amount of OH- added ,a plot of the dependence of the pH of this solution is known a titration curve .There is an inflection point at pH 4.8 in the curve which is the pK of acetic acid. In the area of this pH, a relatively large amount of OH- (or H +) produces little change in pH as the added OH - (or H+ ) reacts with CH 3COOH (or CH3 COO-), respectively. In buffering Weak acids are most effective against changes in pH within 1 pH unit of the pK frequently referred to as pK ± 1, the buffering capacity.
Biological fluids, including the extracellular fluids and cytosol like blood, are buffered. For instance, in healthy individuals the blood pH is carefully controlled at pH 7.4. The major buffering components in most of the biological fluide are the phosphate ion (H2PO4 -, pK 6.82) and the carbonate ion (HCO3- , pK 6.35) because they have pK values in this range. Though, many biological molecules,
Outer membrane
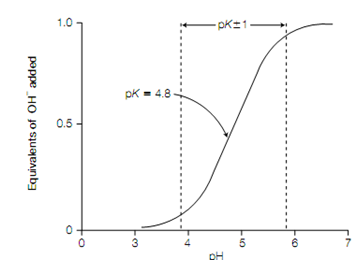
Titration curve of acetic acid.
including proteins, amino acids, nucleic acids and lipids, have multiple acid-base groups that are effective in the physiological pH range (pH 6-8) at buffering.
When working with enzymes, proteins and other biological molecules it is frequently crucial to buffer the pH of the solution in order to ignore denaturation (loss of activity) of the component of interest . In laboratories many buffers are used for this specific purpose. One of the commonest is tris (hydroxy- methyl)aminomethane or TRIS which has a pK of 8.08.