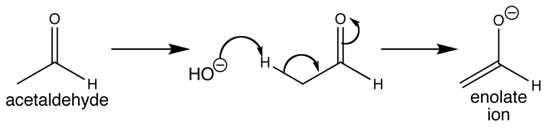
Enolates:
Enols (also termed as alkenols) are alkenes along with a hydroxyl group affixed to one of the carbon atoms creating the double bond. Alkenes along with a hydroxyl group on both of the sides of the double bond are known as enediols. Deprotonated anions of enols are termed as enolates. A reductone is a compound which has an enediol structure along with an adjacent carbonyl-group.
The C=C double bond with adjacent alcohol provides enols and enediols their chemical characteristics, through which they present keto-enol tautomerism. In keto-enol tautomerism, enols interconvert along with ketones or aldehydes.
The terms enol and alkenol are portmanteaus of the terms "alkene" (or just -ene, the suffix given to C=C double bonded alkenes) and "alcohol" (that presents the enol's hydroxyl group).