Single-Phase AC Induction Motors:
If two stator windings of unequal impedance are spaced 90 electrical degrees apart and linked in parallel to a single-phase source, the field generates will appear to rotate. This is known as phase splitting.
In a split-phase motor, a beginning winding is utilized. That winding has a higher resistance and lower reactance than the major winding that was show in the above figure. When the similar voltage VT is applied to the starting and main windings, the current in the main winding (IM) lags behind the current of the starting winding IS. The angle among the two windings is sufficient phase difference to give a rotating magnetic field to generate a starting torque. While the motor reaches 70 to 80% of synchronous speed and a centrifugal switch on the motor shaft opens and disconnects the beginning winding.
Single-phase motors are used for extremely small commercial applications like as buffers and household appliances.
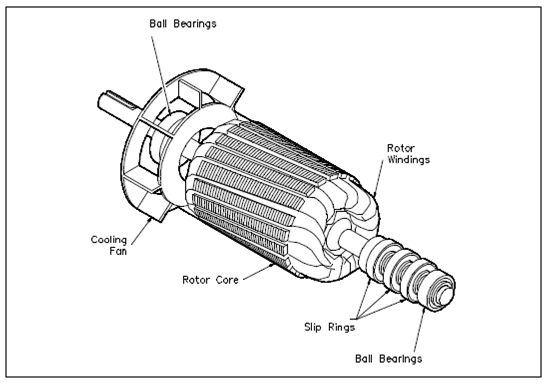
Figure: Wound Rotor