Transformer:
Transformers are utilized widely in AC power systems because they make possible power generation at the most economical level (10-20 kV), power transmission at an economical transmission voltage (400-1000 kV) and power utilisation at most suitable distribution voltages (230/400 V).
Transformers are used for following:
1. Changing voltage and current levels in electric power systems.
2. Matching source and load impedances for maximum power transfer in electronic and control circuits.
3. Electrical isolation (isolating one circuit from another).
Since there are no rotating parts, the construction of transformer is comparatively simple. Transformer is a machine with highest efficiency amongst the electrical machines.
The following are the major parts of a transformer:
1. Magnetic circuit chiefly comprising of limbs and yoke.
2. Electric circuit comprising of windings and insulations mainly.
3. Tank to accommodate the entire assembly, i.e. oil, conservators, cooling devices, etc.
We will define the transformer as :
"A transformer is a static device that consists of two or more than two coils, wound on an air core or a magnetic material core which are electrically isolated but magnetically coupled. It transforms one or more electrical parameters such like current, voltage impedance and so on from one alternating circuit to another."
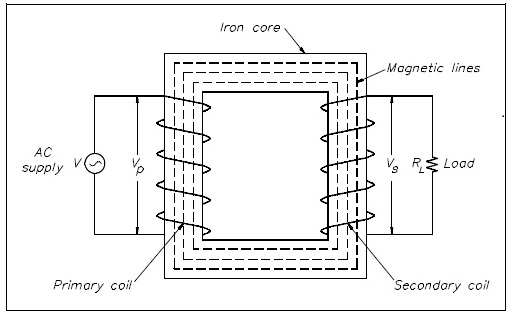
Figure: A Transformer with N1 and N2 Number of Turns in Primary and Secondary Respectively N1 ≠ N2 (Normally)
A transformer, in its simplest form essentially consists of two insulated windings interlinked by a common or mutual magnetic field established in a core of magnetic material. A winding linked to the AC supply is known as primary winding and other winding supplies the load is termed as secondary winding.