Comparison to parallel projections:
In comparison to parallel projections, perspective projections frequently provide a more natural and realistic view of a three-dimensional object like perspective transformation is a transformation from one three space to another three space. In particular case of perspective projection, lines not parallel to the view plane converge to a distant point (called as vanishing point) in the background. While the eye or camera position is close to the object, perspective foreshortening occurs along distant objects appearing smaller in the view plane than closer objects of the same size.
Perspective projections may be divided further into one-point, two-point, & three-point projections. Each of class differs in the orientation of the view plane and the number of vanishing points the unit cube has.
In a one-point perspective, lines of a three-dimensional object along with a major axis converge to a single vanishing point whereas lines parallel to the other axes remain horizontal or vertical in the view plane. To make a one-point perspective view, the perspective transformation is specified by
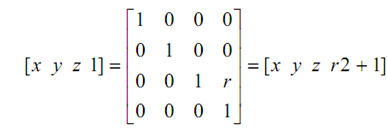
As discussed above, the perspective projection on two-dimensional plane may be obtained by concatenation of orthographic projection and perspective transformation. Thus, the transformation matrix for a perspective projection onto the z = 0 plane would be
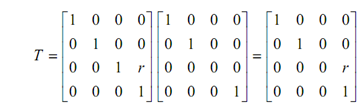
and if the point [x y z 1] is to be projected then it shall be
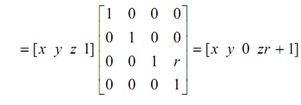
Then
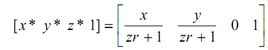
In particular case of one point perspective, there shall be single vanishing point that lies at an equal distance on the opposite side of the plane of projection from the centre of projection. For instance, if plane of projection is at z = 0 and centre of projection is at z = - 1/ r. After that the vanishing point is at z = + 1 /r
A two-point perspective projects an object to the view plane in such manner that lines parallel to two of the major axes converge into two separate vanishing points. To make a two-point perspective, the view plane is set parallel to one of the principal axis instead of a plane.