Measuring volatility is very important as it is a critical input in valuation models. In subsequent chapters we will see the importance of assumed volatility in valuing bonds with embedded options. Also, in measuring the interest rate risk of a position, a combination of duration with yield volatility is used.
Measuring Historical Yield Volatility
Standard deviation or variance is used to measure the yield volatility. We can calculate variance using historical date with the help of the following formula:
Variance = 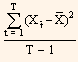 ... Eq. (1)
... Eq. (1)
and
Standard deviation = 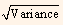
In the above formula, Xt is the observation t of variable 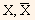 , is the sample mean for variable X, and T is the number of observations in the sample.
, is the sample mean for variable X, and T is the number of observations in the sample.
Our focus is to calculate the change in the daily yield relative to the previous day's yield.
This can be computed as the natural logarithm of the ratio of the yield for two days i.e.,
ln (yt/yt - 1)
Where,
yt = Yield on day t.
yt - 1 = Yield on day t - 1.
The relative change of daily yields computed under simple compounding and continuous compounding is almost same. But, continuous compounding is more popular among market participants.
Multiplying the natural logarithm of the ratio of the two yields by 100 scales gives us the percentage change in daily yields.
Xt = 100 [ln (yt/yt - 1)]
Where,
Xt = % change in yield.
yt = Yield on day t.
yt - 1 = Yield on day t - 1.
Determining the Number of Observations
The sample size, i.e., the number of observations taken, affects the calculation of daily standard deviation. It is difficult to define an ideal sample size as it always depends upon the situation in hand. For example, a portfolio manager who is more concerned about long-term volatility might use 25 days for observation whereas a trader concerned about overnight positions might use only 10 most recent trading days.
Annualizing the Standard Deviation
We can find the annualized standard deviation with the help of the formula given below:
Daily standard deviation x 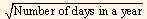
There is a different view regarding the number of days in the year that is to be used in the formula given above. Some market participants use 360 days whereas some use 365 days. There are some market participants who use only trading days i.e., 260 days based on five working days in a week for 52 weeks, while some other participants deduct 10 non-trading holidays too and use 250 days.
Interpreting the Standard Deviation
Assume that standard deviation for the 15 years zero coupon bond is 14%. If the prevailing yield is 8% then the annual standard deviation will be 112 basis points (14 x 8).