Write a short note on dispersion shifted and dispersion flatted fibers?
The dispersion features of a fiber is display below:
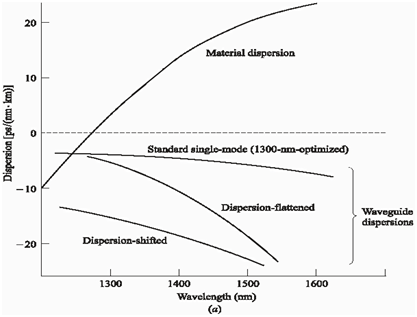
The overall dispersion is the sum of material dispersion and waveguide dispersion.
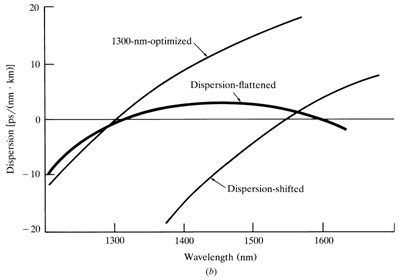
At wavelength larger than the zero material dispersion (ZMD) point within most general fibre designs, the material and waveguide elements are of opposite sign and can thus be made to cancel at a few longer wavelengths. Therefore the wavelength of first order chromatic dispersion can be shifted to the lowest loss wavelength for silicate glass fiber at 1.55 µm to gives both low dispersion and low loss fiber. This may be achieved through such mechanisms as a reduction in the fiber core diameter along with an accompanying raise in the relative or fractional index difference to create so known as dispersion shifted (DS) fiber.
An alternative modification of the dispersion characteristics of single mode fibers includes the achievement of a low dispersion window over the low loss wavelength region among 1.3 µm and 1.6 µm. like fibers, which relax the spectral requirements for optical sources and permit flexible wavelength division multiplexing are called as dispersion flatted (DF) fibers.
A huge variety of single mode fibers refractive index profiles are capable of modifications within order to tune the zero dispersion wavelength point λ0 to a exact wavelength inside a region adjacent to the zero material dispersion (ZMD) point. The simplest profile is in which of a step index fiber, as shown below:
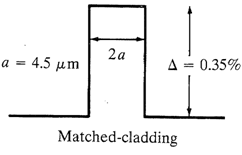
λ0 could be shifted to longer wavelength through altering the material composition of the fiber, which is through increasing the level of germanium doping in the fiber core. We use various profiles for DS as display below:
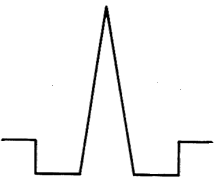
Fig: Triangular profile

Fig: Depressed cladding triangular profile
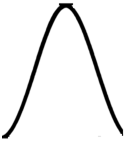
Fig: Gaussian profile
For better results we use advanced refractive index profiles like as
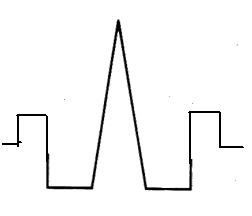
Fig: Triangular profile multiple index
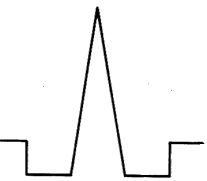
Fig: segmented-core triangular profile design
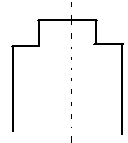
Fig: Dual shaped core design
In dispersion flatted fibers there are two wavelengths of zero dispersion. For getting this window of low dispersion we use various profiles as display below:
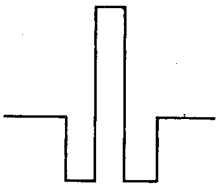
Fig: Double clad
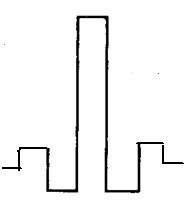
Fig: Triple clad
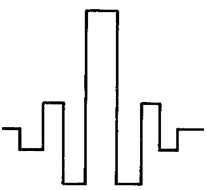
Fig: quadruple clad
The graphical representation of the DS and DF fibres is given below: