As discussed in the earlier section each computer linked to the Internet has a unique address. Let's assume your IP address is 1.2.3.4 & you wish to send a message to the computer along with the IP address 5.7.7.8. The message you wish to send is "Hi computer 5.7.7.8!" Let's assume you've dialed in your ISP from home & the message must be transmitted over the phone line. Thus the message have to be translated from alphabetic text in electronic signals, transmitted onto the Internet, & then translated back into alphabetic text. How is this achieved? Through the use of a protocol stack. Every computer desires one to communicate on the Internet and usually it is built into the computer's operating system (that means Windows, Unix, etc.). On the Internet the protocol stack used is referred to as the TCP/IP protocol stack.
If we were to follow the path that the message "Hello computer 5.9.7.8!" took from our computer to the computer along with IP address 5.6.7.8, it would happen such as:
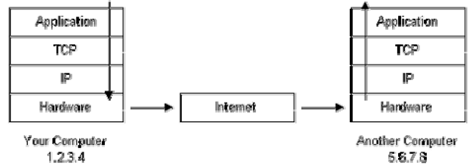
Figure: Environment of the Packet Flow
1. The message would begin at the top of protocol stack on your computer and work its way downward.
2. If the message to be sent is long, every stack layer that the message passes through might break the message up in smaller chunks of data. It is because data sent over the Internet (and most computer networks) are sent in manageable chunks. These chunks of data are known as packets on the Internet,.
3. The packets would go through the Application Layer and continue to the TCP layer. Each of the packets is assigned a port number, which is used through program on destination computer to receive the message because it will be listening on a specific port.
4. After going through the TCP layer, packets proceed to the IP layer. It is where each of the packets receives at its destination address, 5.6.7.8.
5. Now that our message packets contain a port number & an IP address, they are ready to be sent on the Internet. The hardware layer is responsible for turning our packets having the alphabetic text of our message in electronic signals & transmitting them on the phone line.
6. On another end of the phone line your ISP have a direct connection to the Internet. The ISPs router verifies the destination address in each of packet and searched where to send it. Frequently, the packet's next stop is another router. More on routers & Internet infrastructure later on.
7. Eventually, the packets attain computer 5.6.7.8. Here, the packets begin at the bottom of the destination computer's TCP/IP stack & work upwards.
8. As the packets go upwards by the stack, all of the routing data that the sending computer's stack added (like IP address & port number) is stripped from the packets.
9. While the data reaches the top of the stack, the packets has been re-assembled in their original form, "computer 5.6.7.8!"