The Control Unit along with the Main Memory and Arithmetic Logic Unit is called the Central Processing Unit (CPU). The CPU is considered to be the heart of any Computer System.
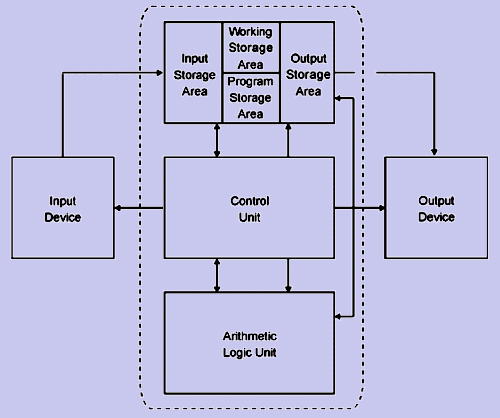
2. Main Memory or Primary Storage: The main memory can be considered to have been divided into four work areas without any fixed physical boundaries.
-
Input Storage Area: Is where the data fed in is held till they are ready to be processed.
-
Working Storage Area: Is where the data are processed and the intermediate results are held.
-
Output Storage Area: Is where the final results of the processing are held until they can be released.
-
Program Storage Area: Is where the processing instructions, i.e. the program, is stored.
In addition to the main memory, most computers have secondary or auxiliary storage capabilities also. Secondary storage devices are centrally connected on- line to the CPU where they serve as reference libraries by accepting data directly to the CPU without human intervention.
Figure 1: Basic Structure of a Computer
 3. 3. |
3. Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU): The Arithmetic and Logic Units of most computers are capable of performing addition, subtraction, division and multiplication as well as logical operations.
The data from primary storage is transferred to the ALU where processing takes place, as per the program instructions. The ALU contains one or more storage locations called registers. The registers provide temporary storage for one or both of the operands that take part in the calculations. After the calculations are over, the results are transferred into the memory.
4. Control Unit: The control unit acts as a central nervous system for all the components of the computer. At the beginning of processing, the first program instruction is selected and fed into the control unit from the program storage area. There it is interpreted and from there signals are sent to other components for necessary action. Other program instructions are then selected and executed in a sequence until the processing is complete.
5. Output Unit: The output unit consists of physical devices to record the results obtained by the computer and present them to the outside world. Most output devices are directed by the control unit, which also causes the necessary information to be supplied to them. Some of the common output devices are: Visual Display Unit (VDU), Printers, Card Punching Machines, Magnetic Tape Drives, Magnetic Disk Drive, Floppy Disk Drive, Graph Plotters, etc.