The Work Systems Framework - Information System
Adler writing in 1992 used the phrase 'stumbling backwards into the future' to describe the neglect organisations at that time were displaying towards the incorporation of technology into their operations highlighting the problem as lack of consideration for the complexities of the three-way interaction between technology, people and the wider organisation. Bringing this idea up to date and to help us build information systems effectively into our business a model is required that involves all aspects of the organisation in the process of analysis of the work that goes on in our operations.
The diagram overleaf illustrates one model that can be used to aid in our analysis that takes into consideration all elements involved in doing the work.
A work system is a system in which humans and/or machines perform a business process using information, technology and other resources to produce products and services for internal or external customers.
To use this tool effectively first we need to define the unit that is the work system we are analysing. The work system is usually more that just one process. It may be a set of complementary processes that exist within the overall operation that work towards a common goal.
It may also extend beyond traditional boundaries of the operations function because it includes the customers and other organisational elements. Therefore the work system maybe smaller than the organisation but is (usually) larger than a single process. The work system encourages us to look beyond organisational or functional boundaries and consider all value-adding elements simultaneously and equally. However, while saying this, the operational process should always remain at the core of the work system.
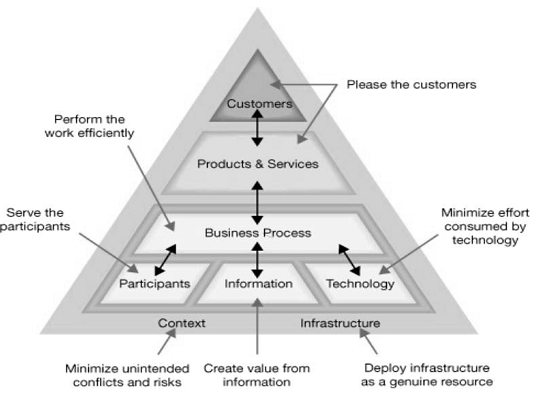
The elements of the work system are:
- Customers - people who use and receive direct benefits from the products and services produced by the work system. Customers maybe external to the organisation or internal to the organisation.
- Products and services - the combination of tangible and intangible things that the work system outputs for the consumption of its customers.
- Business process - a set of correctly sequenced work steps or activities.
- Participants - people that perform tasks within the system.
- Information - that is used by the participants to complete their tasks.
- Technology - hardware, software or any other tools and equipment used by the participants to complete their work.
- Context - the organisational, competitive, technical and regulatory realm.
- Infrastructure - the shared human and technical resource that the work system relies on even although these resources exist out with the system itself. This includes support staff such as training and maintenance.
This framework is useful to operations managers when considering IS implementation because it helps define the relationship between the overall work system including customers, employees, etc. and the IS used to support it. Considering all of these work system elements in tandem will avoid the optimisation of one element at the detriment of another eg the implementation of a fully-integrated, hi-tech IS at the expense of flexibility and use-ability.
Each element of the work system has a guiding principle that should be considered when designing the work system to ensure this element is optimised:
- Please the customer with the correct products and services.
- Ensure the business process performs efficiently.
- The participants should be served by the work system.
- The information should add value.
- The technology used should consume minimum effort.
- The infrastructure should be deployed as a genuine resource.
- The context should minimise conflict and risk.