Why Deficiency of Folate take place?
If there is inadequate dietary folate, the activity of both the DNA and the methylation cycles, described above, will be reduced. A decrease in the former will reduce DNA biosynthesis and thereby reduce cell division. Although this will be seen in all dividing cells, the deficiency will be most obvious in cells that rapidly divide, including for example red blood cells, thereby producing megaloblastic anaemia characterized by large, abnormally nucleated erythrocytes, as can be seen in Figure, that accumulate in bone marrow.
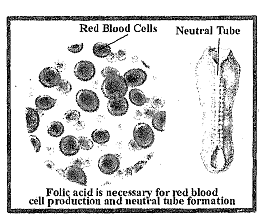
Taken together, the effects caused by the reduction in the DNA cycle result in an increased susceptibility to infection, a decrease in blood coagulation, and intestinal malabsorption. Folate deficiency will also decrease the flux through the methylation cycle but the DNA cycle may be more sensitive. The most obvious expression of the decrease in the methylation cycle is an elevation in plasma homocysteine. This is use to a decreased availability of new methyl groups provided as 5- ethyltetrahydrofolate, necessary for the remethylation of plasma homocysteine. Previously it was believed that a rise in plasma homocysteine was nothing more than a biochemical marker of possible folate deficiency. However, there is increasing evidence that plasma homocysteine concentration, if only moderately elevated, is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease and stroke. Interruption of the methylation cycle resulting from impaired folate status or decreased vitamin B12 or vitamin B6, status may have serious long-term risks.
Pregnant women are at a higher risk of developing folate deficiency because of increased demand for folate. In addition to megaloblastic anaemia, inadequate folate intake is associated with poor pregnancy outcomes. Impaired folate status is associated with increased risk of pre-term delivery, infant low birth weight and foetal growth retardation. An elevated maternal homocysteine concentration leads to increased habitual spontaneous abortion and pregnancy complications (e.g. abruptio placentae or placental infarction with foetal growth retardation and pre eclampsia) which increase the risk of low birth weight and preterm delivery. Folate deficiency is associated with Neural Tube Defects (NTDs) as highlighted in Figure. During pregnancy, there is an increased risk of foetal neural tube defects (NTDs), with risk increasing 10-fold as folate status goes from adequate to poor. Between days 21 and 27 post-conception, the neural plate closes to form what will eventually be the spinal cord and cranium. Spina bifida, anencephaly and other similar conditions are collectively called NTDs. They result from improper closure of the spinal cord and cranium, respectively, and are the most common congenital abnormalities associated with folate deficiency.
Multivitamin supplements containing folic acid reduce the risk of NTDs. It is now agreed that a supplement of 400 pg of folic acid taken near the time of conception will prevent most NTDs. The recommendation to prevent recurrence in women with a prior NTD birth remains 4 mg/day. Folate status is also related to birth defects other than NTDs such as cleft lip and palate, limb deficiencies and conotruncal or the outflow tract defects of the heart.
In addition, evidence also suggests a link between colorectal cancer and dietary olate intake and folate status. Low folate status has been associated with an increased risk of colorectal cancer. Thus, it is evident that folate is very essential for good health. The next question that comes to mind then is there a risk associated with excessive consumption of folate as well. Read the next sub-section on toxicity and find out.