Q. What is the Structure of diborane?
The structure of diborane is of great interest since it cannot be explained on the basis of simple theories of bonding. As mentioned earlier, there are not enough valence electrons in B2H6 to form the expected number of covalent bonds, in other words, B2H6 is an electron-deficient compound. Since boron atom has three unpaired electrons in the outermost orbit in the excited state, it can form three covalent bonds. If each of the boron atoms in diborane links itself to three hydrogen atoms, there will be no electrons left to form a bond between the two boron atoms. Thus, diborane cannot have an ethane type structure as shown in the margin.
Diborane, B2H6, has been found to possess a bridge structure (Fig. 6.2) in which each B atom is bonded to two H atoms called terminal H atoms by regular electron-pair bonds. The resulting two BH, fragments are bridged by two H atoms as indicated by electron diffraction studies and by Raman and infrared spectroscopy. The two boron atoms and the four terminal hydrogen atoms lie in the same plane while the two bridging hydrogen atoms lie in a plane perpendicular to this plane as shown in Fig. 6.2. The bridging hydrogen atoms prevent rotation between the two boron atoms.
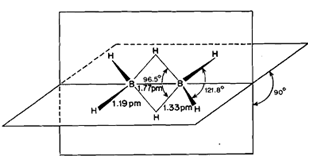
In the bridge structure, diborane has eight bonds but there are 12 electrons available for bonding, three per B and one per H. Hence, all the bonds in the molecule cannot be electron-pair bonds which would require 16electrons for the structure in Fig. 6.2. The terminal B-H bond lengths are the same as the bond lengths in non-electron deficient compounds. This means that the four terminal B-H bonds are normal electron pair bonds accounting for a total of eight electrons. Thus, electron deficiency must be associated with the bridging B-H-B bonds in which a pair of electrons binds three atoms, viz., B, H and B. Therefore, these bridging B-H-B bonds are called three centre electron pair bonds abbreviated as 3c-2e.