Q. A compound microscope consists of an objective lens of focal length 2.0cm and an eye piece of focal length 6.25cm separated by a distance of 15cm.How far from the objective should an object be placed in order to obtain the final image at (a) the least distance of distinct vision (25cm),and(b)at infinity? What is the magnifying power of the microscope in each case?
Answer
A Focal length of the objective lens f1 = 2.0cm
A Focal length of the eye piece f2 = 6.25cm
Distance among the objective lens and the eye pieced = 15cm
(a)Least distance of distinct vision d' = 25cm
∴ Image distance for the eye piece v2 = -25cm
An Object distance for the eye piece = u2
As-per to the lens formula we have the relation
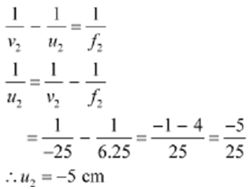
Image distance for the objective lens v1 = d + u2 = 15 - 5 = 10 cm
An Object distance for the objective lens = u1
As-per to the lens formula we have the relation
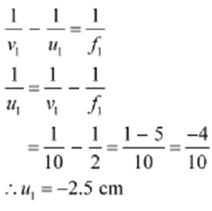
Magnitude of the object distance u1 =2.5cm
A magnifying power of a compound microscope is given by the relation:
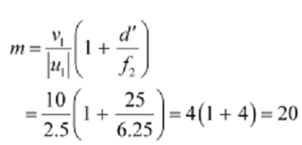
Therefore the magnifying power of the microscope is 20.
(b) The absolute image is formed at infinity.
∴Image distance for the eye piece v2 = ∞
An Object distance for the eye piece = u2
As-per to the lens formula we have the relation:
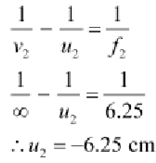
A Image distance for the objective lens v1=d + u2= 15-6.25 = 8.75cm
An Object distance for the objective lens=u1
As-per to the lens formula, we have the relation
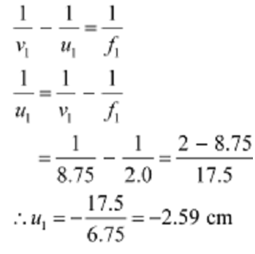
A Magnitude of the object distance |u1|=2.59cm
A magnifying power of a compound microscope is given by the relation
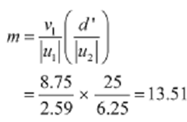
Therefore the magnifying power of the microscope is 13.51